 |
ChemicalFemPhysics
The GeMA Standard Chemical FEM Physics Plugin
|
 |
ChemicalFemPhysics
The GeMA Standard Chemical FEM Physics Plugin
|
The Chemical FEM physics is the responsible for providing an implementation for the multispecies reactive solute transport equation that can be used together with the Fem process to solve the steady state and transient reactive solute transport through a porous media such as rock, in 2D and 3D. The main equation solved by this physics is:
\[ k_i \frac{\partial C_i}{\partial t} = \nabla\cdot(D \nabla C_i)-v\nabla C_i + R_i \]
where:
In order to solve the chemical problem we need to state appropiate initial and boundary conditions. Two types of boundary conditions be emplemented in GeMA, Dirichlet (Prescribed concentration of species in \(mol/m3\)) and Neumann (prescibed concentration flow in \(mol/m^3*s\)).
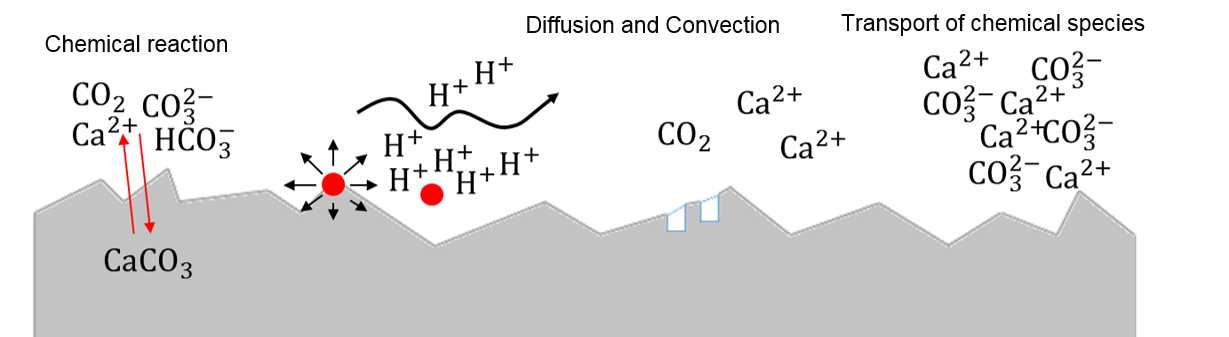
The Chemical FEM physics plugin supports the following formulations:
The FEM discretization of multispecies reactive solute transport equation used by the Chemical Fem physics plugin is based on the book Fundamentals of the Fundamentals of the Finite Element Method for Heat and Fluid Flow by Roland W. Lewis, Perumal Nithiarasu and Kankanhalli N. Seetharamu, 2004.
A reference manual documenting the set of state variables and material properties expected by the plugin, along with all of its supported configuration and result options can be found here.
Several example simulations involving steady state and transient flow calculations are available at the examples directory provided with the GeMA instalation. A summary of those examples can be found here.
 1.8.15
1.8.15